Photoaging vs Chronoaging: Types of Skin Aging
Scientific explanation of skin aging mechanisms and their differences
Overview
Skin aging occurs under the influence of two main factors: photoaging (external factors) and chronoaging (internal factors). Understanding the difference between them is key to effective prevention and treatment.
Key Statistics
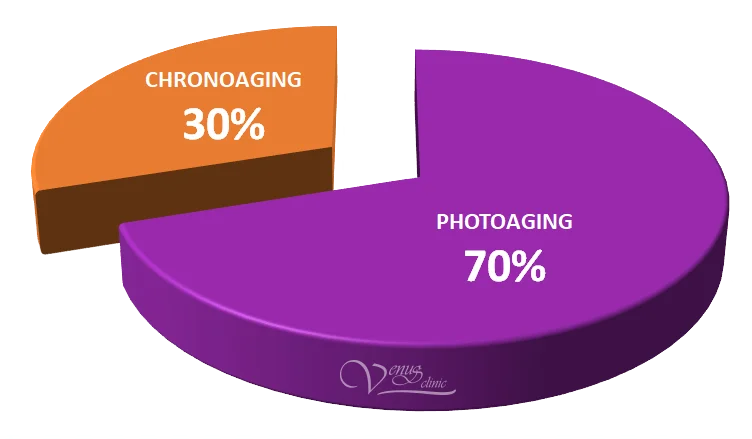
70-80% of skin aging occurs due to photoaging
20-30% of skin aging occurs due to chronoaging

Photoaging
Definition
Photoaging — is premature skin aging caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or artificial UV light sources.
Main characteristics of photoaging:
- External cause: ultraviolet radiation
- Can be prevented: with sun protection products
- Reversible process: partially treatable
- Speed: depends on intensity of UV exposure
Clinical manifestations of photoaging:
🔸 Pigment changes:
- Solar lentigo
- Freckles
- Uneven skin tone
- Age spots
🔸 Vascular changes:
- Telangiectasias
- Rosacea
- Dilated capillaries
- Spider veins
🔸 Structural changes:
- Fine wrinkles
- Rougher skin texture
- Reduced elasticity
- Enlarged pores
🔸 General changes:
- Skin dryness
- Reduced turgor
- Yellowish tint
- Actinic keratosis
Chronoaging (Chronoaging)
Definition
Chronoaging — is a natural, genetically programmed process of skin aging that occurs with age independently of external factors.
Main characteristics of chronoaging:
- Internal cause: genetic aging program
- Cannot be stopped: natural process
- Can be slowed down: with proper care
- Speed: individual, depends on genetics
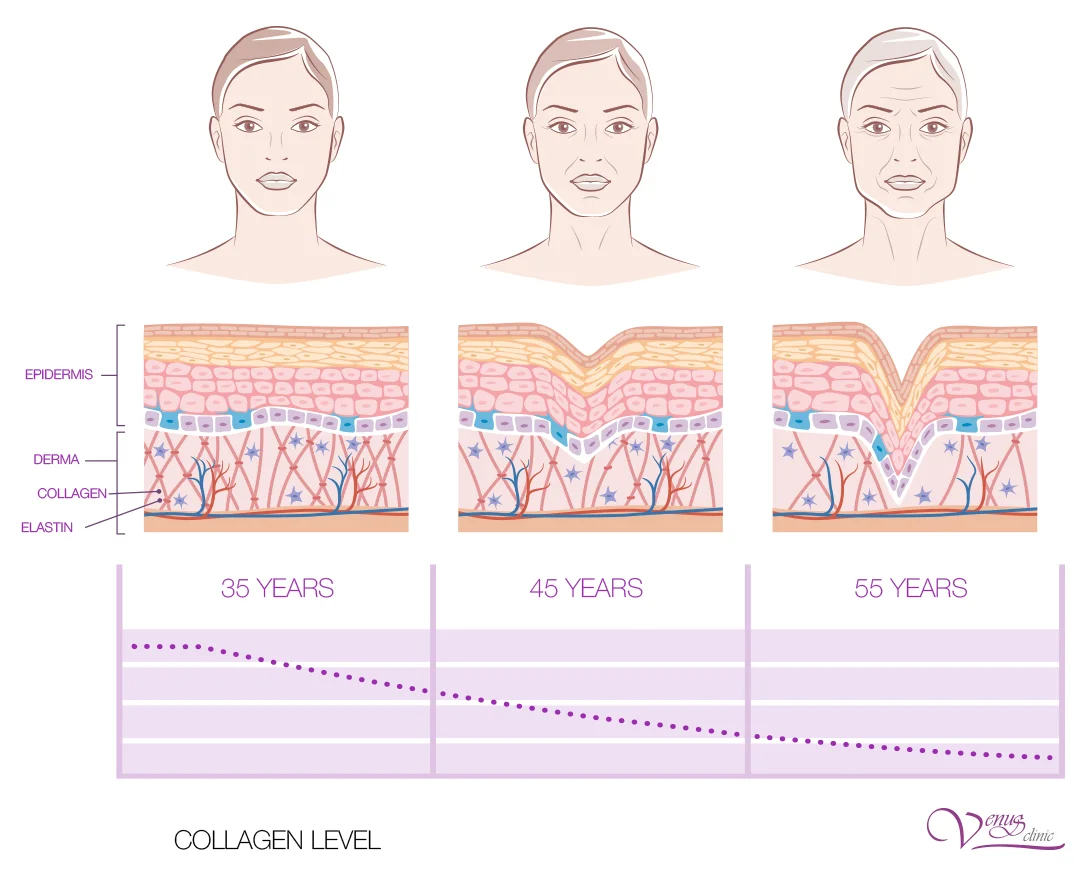
Mechanisms of chronoaging:
Decreased collagen synthesis
After age 25, collagen synthesis decreases by 1-2% annually
Elastin degradation
Elastin fibers lose elasticity and fragment
Slowed cellular renewal
Epidermal renewal cycle extends from 28 to 45+ days
Decreased hyaluronic acid
Ability to retain moisture decreases by 6% each decade
Clinical manifestations of chronoaging:
- Gradual loss of skin elasticity
- Decreased dermal thickness
- Formation of static wrinkles
- Reduced natural hydration
- Slower healing
- Decreased soft tissue volume
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | PHOTOAGING | CHRONOAGING |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | UV radiation | Genetic program |
| Speed | Fast, depends on exposure | Gradual, constant |
| Localization | Exposed areas (face, hands) | Entire skin surface |
| Main manifestations | Pigmentation, vessels, fine wrinkles | Deep wrinkles, dryness, laxity |
| Prevention | Sun protection, UV avoidance | Proper care, healthy lifestyle |
| Reversibility | Partially reversible | Irreversible, can be slowed |
| Impact share | 70-80% | 20-30% |
Impact of UVA and UVB Rays
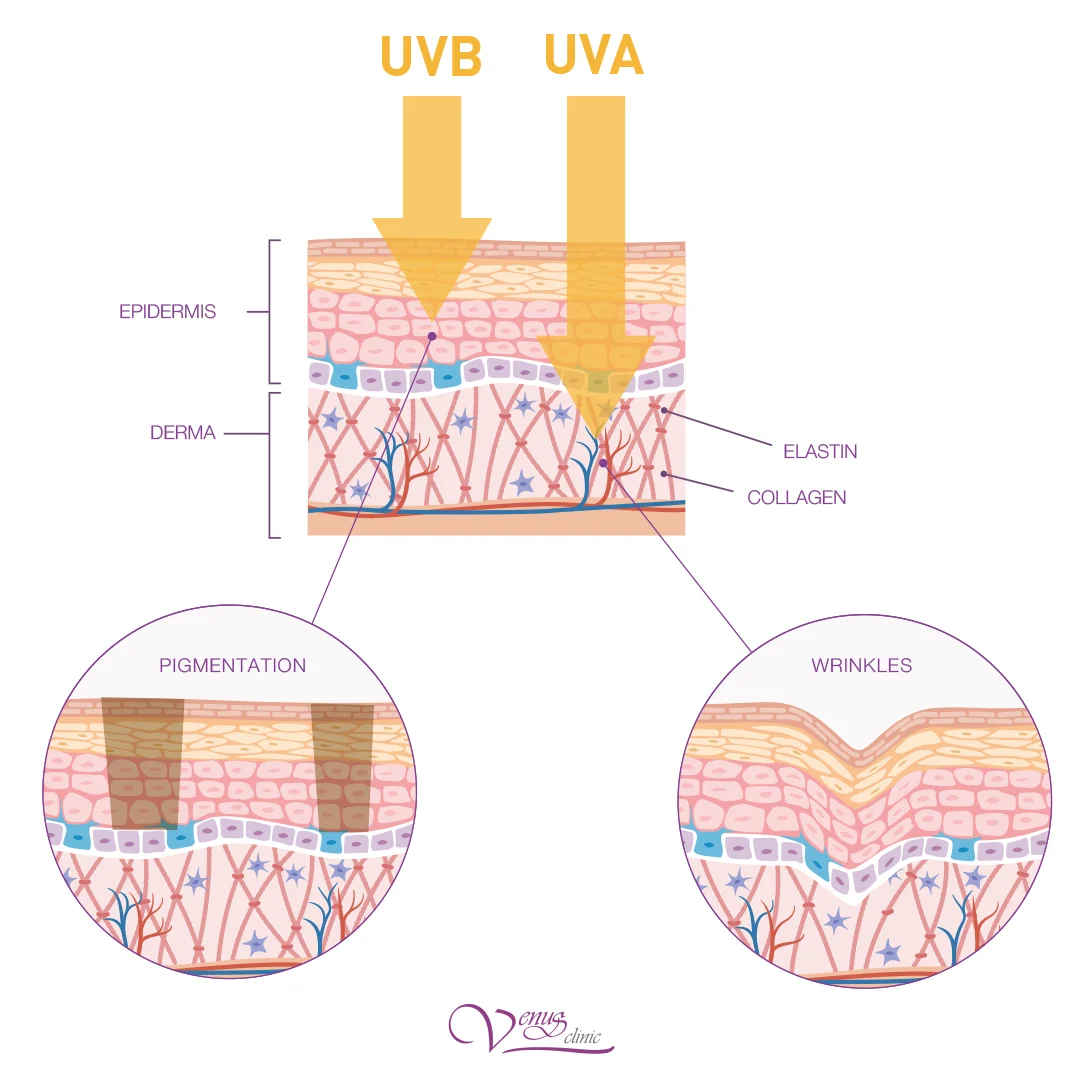
🔶 UVB Rays (280-315 nm)
Characteristics:
- Shorter wavelengths
- Affect the epidermis
- Active in summer
- Do not penetrate glass
Damage:
- Age spots
- Solar lentigo
- Actinic keratosis
- Sunburns
Target:
Melanocytes (pigment cells), keratinocytes
🔷 UVA Rays (315-400 nm)
Characteristics:
- Longer wavelengths
- Penetrate into dermis
- Present year-round
- Penetrate through glass
Damage:
- Fine wrinkles
- Telangiectasias
- Elastosis
- Reduced elasticity
Target:
Collagen and elastin
UV Radiation Protection
Important: For complete protection, you need broad-spectrum sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays with SPF of at least 30.
Scientific Research and Statistics
Research on aging factor impacts:
American Academy of Dermatology Study
- Photoaging: 70-80% of all age-related skin changes
- Chronoaging: 20-30% of all age-related skin changes
- Conclusion: Most signs of aging can be prevented
Journal of Investigative Dermatology Study
- Daily use of SPF 30+ reduces photoaging by 24%
- People who regularly protect themselves from the sun look 7-10 years younger
- Even partial use of sun protection significantly slows photoaging
Stanford University Study (2012)
- Photorejuvenation procedures can influence gene expression
- Regular photorejuvenation slows both photo- and chronoaging
- Cells begin to "work" as they do at a young age
Prevention and Treatment
Photoaging Prevention
Daily Protection:
- SPF 30+ every day
- Reapplication every 2 hours
- Protective clothing and hats
- Avoiding sun from 10:00 AM to 4:00 PM
Skincare:
- Antioxidants (vitamin C, E)
- Retinoids for restoration
- Regular moisturizing
- Gentle cleansing
Slowing Chronoaging
Lifestyle:
- Balanced nutrition
- Regular physical exercise
- Adequate sleep (7-9 hours)
- Stress management
Nutraceuticals:
- Collagen and elastin
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Superoxide dismutase: GliSODin
- Coenzyme Q10, resveratrol
Treatment Results for Different Types of Aging
Want to stop photoaging?
Schedule a consultation at Venus Clinic and discover how modern methods can help your skin
Frequently Asked Questions
What is photoaging?
Photoaging is premature skin aging caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. It accounts for 70-80% of all age-related skin changes and manifests as age spots, dilated blood vessels, and wrinkles.
What is chronoaging?
Chronoaging is a natural, genetically programmed process of skin aging that accounts for 20-30% of all age-related changes. It manifests as gradual loss of collagen, elastin, and decreased cellular renewal.
What is the difference between UVA and UVB rays?
UVA rays (315-400 nm) penetrate into the dermis and cause wrinkles and telangiectasias. UVB rays (280-315 nm) affect the epidermis and cause age spots and sunburns.
Can photoaging be prevented?
Yes, photoaging can be significantly slowed or prevented through daily use of SPF 30+ sunscreens, avoiding active sun exposure, and proper skincare.
What are the most effective photoaging correction methods?
The most effective methods are BBL photorejuvenation, laser procedures, fractional skin resurfacing, chemical peels, and injection techniques. The choice of method depends on the type and degree of skin damage.
Scientific Sources
- Gilchrest BA. Photoaging. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(E1):E2-6.
- Quan T, Fisher GJ. Role of Age-Associated Alterations of the Dermal Extracellular Matrix Microenvironment in Human Skin Aging. Gerontology. 2015;61(5):427-34.
- Flament F, Bazin R, Laquieze S, et al. Effect of the sun on visible clinical signs of aging in Caucasian skin. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:221-32.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Sunscreen FAQs. 2019.
- Chang ALS, Bitter PH Jr, Qu K, et al. Rejuvenation of gene expression pattern of aged human skin by broadband light treatment. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(2):394-402.