Photosensitizers in Laser Hair Removal and Laser Cosmetology
Photosensitizers are substances that increase skin sensitivity to light. Before laser procedures, it's important to know which medications can cause unwanted reactions. At Venus Clinic, we always conduct detailed consultations to ensure the safety of our patients.
What are Photosensitizers
Photosensitizers are medical drugs, cosmetic products, or natural substances that can increase skin sensitivity to light. This can lead to phototoxic or photoallergic reactions during laser procedures.
Classification of Radiation Ranges
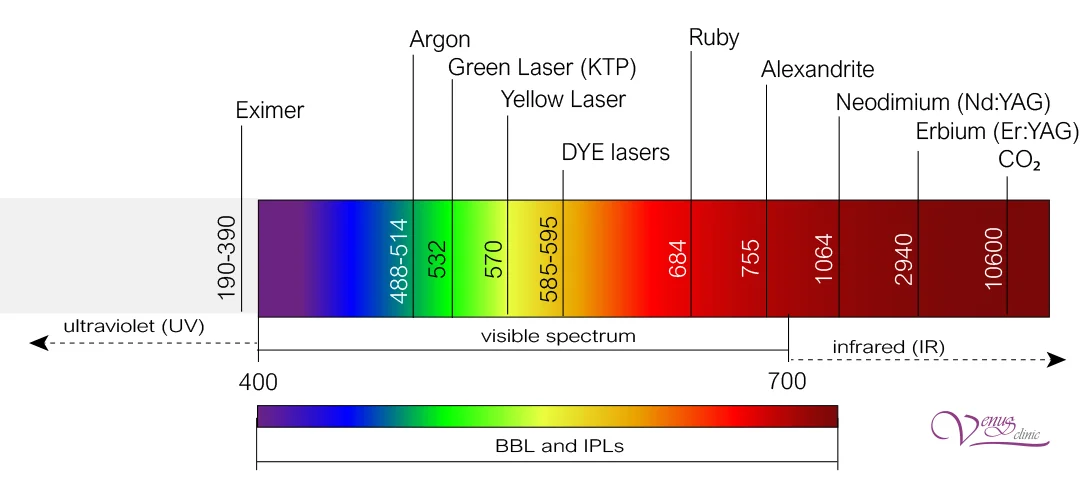
Radiation Spectrum:
- 100-280 nm - UVC (ultraviolet C)
- 280-315 nm - UVB (ultraviolet B)
- 315-400 nm - UVA (ultraviolet A)
- 400-740 nm - visible range
- >740 nm - infrared range
List of Photosensitizing Medications
Below is a detailed list of drugs that may affect the results of laser procedures:
Antibiotics
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, etc.) | ✓ | - | 280-330 nm |
| Tetracycline (doxycycline) | ✓ | - | 320-425 nm |
| Sulfonamides (trimethoprim) | ✓ | - | UVB |
| Dapsone | ✓ | - | UV |
| Chlorhexidine | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Minocycline | ✓ | - | - |
Chemotherapeutic
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-fluorouracil | ✓ | ✓ | UVA |
| Vinblastine | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Dacarbazine | ✓ | - | UVA |
Cardiac Medications
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amiodarone | ✓ | - | 335-460 nm |
| Nifedipine | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Quinidine | ✓ | ✓ | UVA |
| Diltiazem | ✓ | - | UVA, UVB |
Diuretics
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemide | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Thiazides | ✓ | ✓ | UVA |
Hypoglycemic (Sugar-lowering)
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonylurea | ✓ | ✓ | UVA |
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Naproxen | ✓ | - | 310-325 nm |
| Ketoprofen | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Celecoxib | ✓ | - | UVA |
Retinoids
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isotretinoin | ✓ | - | UVA |
| Acitretin | ✓ | - | UVA |
Neuroleptics
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenothiazines | ✓ | ✓ | UVA |
| Thioxanthenes | ✓ | - | UVA |
Antidepressants
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tricyclic antidepressants | ✓ | - | UVA |
Antifungal
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Itraconazole | ✓ | ✓ | - |
| Voriconazole | ✓ | - | UVA |
Hypolipidemic (Cholesterol-lowering)
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atorvastatin | ✓ | ✓ | UVB |
Steroids
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone | ✓ | - | UVA |
Antiviral
| Name | Phototoxic Action | Photoallergy | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acyclovir | ✓ | - | UVA |

Vitamins and Laser Hair Removal
Most vitamins are safely combined with laser hair removal at Venus Clinic.
B Group Vitamins
B group vitamins do not have photosensitizing effects on the skin. This also applies to other water-soluble vitamins: vitamin C, folic acid, and biotin.
Vitamin A and Retinoids
Vitamin A is not a photosensitizer, but retinoids may impair wound healing after laser procedures.

Lasers and Photosensitization
Lasers used in Venus Clinic cosmetology operate in visible and infrared ranges:
Lasers in Visible Range (400-740 nm)
- KTP (green laser) - 532 nm
- Dye lasers - 585-595 nm
- Ruby laser - 694 nm
Lasers in Infrared Range (755-10600 nm)
- Alexandrite laser - 755 nm
- Diode lasers - 800-910 nm
- Neodymium lasers Nd:YAG - 1064 nm
Recommendations for Patients
Before laser procedures:
- Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking
- Do not hide information about supplements and vitamins
- Be sure to mention the use of cosmetics with photosensitizers
- Consult with your doctor about the possibility of discontinuing the medication
Need a Consultation?
Before starting laser procedures, be sure to consult with experienced doctors at Venus Clinic. We will conduct a detailed analysis of your medications and ensure maximum safety of procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are photosensitizers?
Photosensitizers are substances that increase skin sensitivity to light. They can cause phototoxic or photoallergic reactions when interacting with ultraviolet or visible light, making laser procedures dangerous.
Can I have laser hair removal while taking antibiotics?
It depends on the type of antibiotic. Quinolones, tetracyclines, and sulfonamides are photosensitizers and can cause burns during laser procedures. Be sure to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking.
How long should I wait after discontinuing photosensitizers?
The waiting period depends on the drug: antibiotics — 7-14 days, retinoids — 2-4 weeks, amiodarone — up to 6 months. The exact term is determined by the doctor individually depending on dosage and duration of intake.
Do vitamins affect laser procedures?
Most vitamins are safe during laser procedures. Water-soluble vitamins (B, C) do not accumulate in the body. Vitamins A, D, E are also not photosensitizers, but retinoids may impair healing.
What natural photosensitizers exist?
Natural photosensitizers include citrus essential oils (bergamot, lemon, lime, grapefruit), parsley, celery, parsnip. Concentrated essential oils are especially dangerous before sun or laser exposure.
Can I have photorejuvenation while taking cardiac medications?
Many cardiac medications (amiodarone, nifedipine, quinidine) are photosensitizers. Procedures are possible only after consultation with a cardiologist and cosmetologist, temporary discontinuation or drug replacement may be required.
Which lasers are safer for photosensitization?
Infrared range lasers (755-1064 nm) are less dangerous than UV radiation. However, caution is needed even with them. IPL systems with filters above 400 nm are also relatively safe, but risk remains.
How to prepare for laser procedure if taking medications?
Be sure to inform your doctor about all medications 2-4 weeks before the procedure. Do not discontinue vital medications on your own. The doctor will develop an individual preparation plan or suggest alternatives.
What to do if reactions appear after laser procedure?
If unusual reactions appear (severe redness, swelling, blisters), immediately contact your doctor. Apply cold compresses, avoid sun, do not use aggressive products. A photosensitizing reaction is possible.
Can I combine different laser procedures while taking medications?
When taking photosensitizers, it's better to avoid any laser procedures. If the drug is vital, only individual gentle procedures with special safety measures are possible after careful risk assessment.
Venus Clinic - leading laser cosmetology clinic in Kyiv. Our specialists have many years of experience working with photosensitizers and safe laser procedures.
Book a Consultation
Venus Clinic - leading laser cosmetology clinic in Kyiv. Our specialists have many years of experience working with photosensitizers and safe laser procedures.
References
- Kerstein R, Lister T, Cole R (2014) Laser therapy and photosensitive medication: a review of the evidence. Lasers Med Sci 29(4): 1449-52