Retinol (vitamin A)
Retinol is vitamin A, a fat-soluble vitamin that is involved in many metabolic processes in the body: stimulates cell division, improves healing of skin and mucous membranes, improves immunity, is essential for vision.

Sources of Retinol
In the body, retinol is synthesized from β-carotene, which we get from food. Beta-carotene is found in vegetables (carrots, spinach, bell peppers). The most important source of vitamin A is fish oil and liver, as the combination of retinol with fats increases its absorption.
Due to the low absorption of retinol from plant foods, vegans may be chronically deficient in vitamin A.
Caveats
Retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin. Since it is one of the important vitamins for the life of our body, the body is able to accumulate it for future use. Therefore, excessive intake of vitamin A by mouth can cause negative consequences for the body.
Vitamin A, when taken orally in large doses, can accumulate and can have a negative effect on the development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, it is recommended that you stop taking vitamin A and systemic retinoids at least 3 months before the intended pregnancy. Take vitamin complexes with vitamin A before and during pregnancy and lactation only as directed by your doctor!
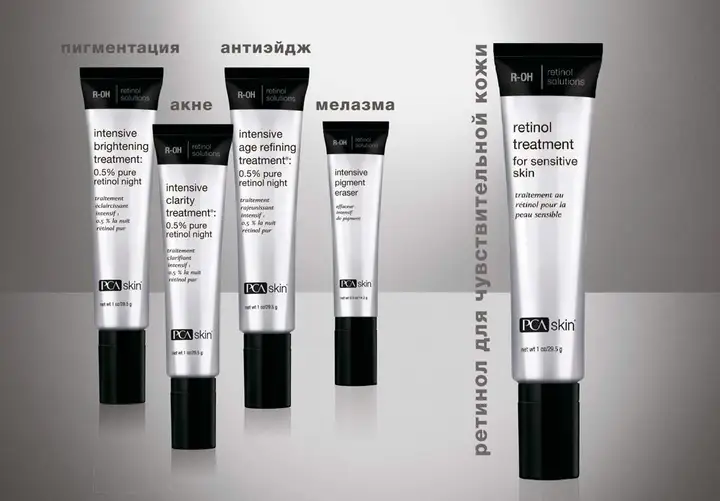
Retinol in cosmetology and dermatology
In dermatology, retinol is used to improve wound healing, in the treatment of acne, psoriasis. For the treatment of acne, local forms in the form of creams are used, as well as systemic forms - Roacutan.
Retinol is one of the few ingredients in cosmetology with a clinically proven anti-aging effect. When applied to the skin, retinol is more potent than when taken orally. The uniqueness of the retinol effect is due to the effect on the DNA of cells, due to which such mechanisms are triggered as the formation of new collagen fibers, the synthesis of hyaluronic acid, a decrease in the production of melanin (lightening of pigmentation), the normalization of the sebaceous glands, and an increase in the renewal of epidermal cells.
Read in detail - Retinoic peeling.