Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a viral infection caused by the human papillomavirus, depending on the species, it can manifest itself as harmless skin rashes or cause cancer of the cervix and other organs.
HPV types and routes of transmission
There are over 100 types of human papillomavirus.
The virus parasitizes the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes. It manifests itself in the form of superficial formations on the skin, mucous membranes of the vulva, vagina, cervix, anus or glans penis, as well as mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes and larynx.
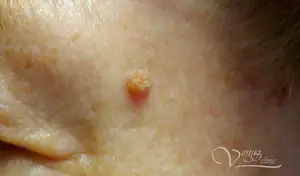
About 60 types of HPV cause skin lesions in the form of warts, papillomas.
The remaining 40 types have sexual transmission and are transmitted during intercourse. In such cases, the lesions are localized on the mucous membranes of the mouth, anus and genitals.
HPV manifestations
HPV infection often causes no symptoms and the body clears the infection on its own over several years. Many people don't know they are infected.
High risk symptoms
It is not uncommon for a high-risk HPV infection to last longer. This can cause changes in the cells of the cervix that can lead to cancer, including cancer of the vulva. The same can cause abnormal changes in the cells of the penis and anus, but this rarely happens.
Low Risk Symptoms
The symptoms of low-risk HPV infection are warts. The type of warts you get will depend on which HPV you have.
- Genital warts. These are either flat spots or raised irregularities. In women, they usually grow on the vulva, but can also appear on the anus, cervix, or vagina. In men, they are localized on the penis, scrotum or anus.
- Simple warts. This type of lesion usually appears on the hands and fingers.
- Plantar warts. Plantar warts are hard, grainy, painful formations that lie on the feet.
- Flat warts. These are slightly raised, flat-topped formations. They can be localized anywhere, more often on the face and legs.
HPV causes and risk factors
Human papillomavirus infects you by entering your body through a cut, scratch or injury to your skin. Infection can occur from skin-to-skin contact, vaginal, anal, or oral sex. You can pass HPV to your baby if you have genital warts during pregnancy. In rare cases, this can lead to tumor growth in the child's larynx.
Warts are contagious. You can get infected by touching or touching someone else's wart.
Risks that increase your chances of getting HPV infection include:
- Damaged skin. Areas of the skin that are injured have a greater risk of infection with warts.
- Direct contact. If you touch someone else's warts or come in contact with surfaces that have touched the warts, you could get HPV.
- Number of sexual partners. The more sex partners you have, the higher your risk of contracting HPV. Having sex with someone with many partners also increases your risk.
- Age. Children are more likely to contract simple warts. Genital warts are more common in adolescents and young adults.
- Weak immune system. If you have a condition such as HIV or AIDS, or are on treatment that weakens your immune system, you are more likely to contract HPV.
HPV Diagnosis
A doctor can diagnose HPV by the presence of a wart. But there are also a few tests they can use if there are no obvious symptoms.
- Vinegar test. A vinegar solution is applied to the genital area. If HPV is present, the lesions will turn white.
- Smear from the cervix. Laboratory test for abnormal cells. Abnormal cells can cause cancer.
- DNA test. If you are a woman over 30 years old, your doctor may recommend this test along with a Pap test. The DNA of the cervical cells is tested to see if there is a type of HPV that can lead to cancer.
HPV Treatment
Warts can go away without treatment, especially in children. Medication:
- Salicylic acid. Apply a wart. They destroy the wart one layer at a time. You shouldn't use this on your face.
- Imiquimod. It is a prescription cream that helps the immune system get rid of HPV. This can cause redness and swelling around the area of application.
- Trichloroacetic acid. Used for warts on the palms, feet and genitals. This can irritate the skin.
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, surgical treatment is prescribed:
- Surgitron Surgery
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen
- Electrocoagulation
- Laser papilloma removal ensures optimal cosmetic effect without unnecessary damage to healthy tissues
- For HPV in the cervix, the doctor may use a laser in conjunction with a colposcopy to find and remove abnormal cells