Melasma: causes, diagnosis and treatment
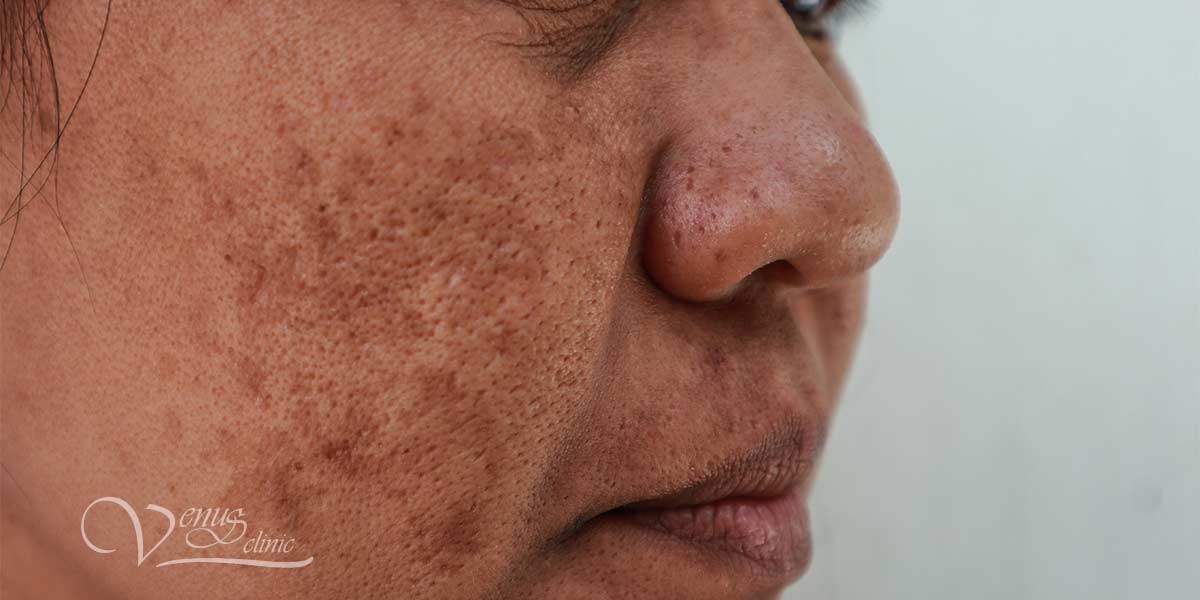
Melasma, melasma - a violation of the pigmentation of the skin of the face with an increase in the formation of melanin with the most frequent localization in the upper part of the cheeks, bridge of the nose, on the forehead, upper lip. May affect 50% of women during pregnancy.
Women are more likely to suffer from melasma than men; appears between the ages of 30-40. Persons with darker skin or a good reaction to the sun (who tan well) tend to be more prone. Most often it is localized in the upper part of the cheeks, the bridge of the nose, on the forehead, upper lip; can occur in 50% of women during pregnancy. Melasma darkens under sunlight or any other source of ultraviolet radiation - tanning beds.

Melasma is also known as the "pregnancy mask" - chloasma.
The difference between melasma and chloasma
In melasma, unlike chloasma, age spots can appear in people at any age, regardless of gender. Pigmented spots resulting from solar irradiation - the solar form (Melasma solare), with liver pathologies - the hepatic form of melasma (Melasma hepatica), which differs from others in the localization of age spots mainly on the lateral surfaces of the neck, the absence of clear boundaries and often a mesh of telangiectasias. See laser vascular removal in detail.
Melasma has a tendency to change the intensity of pigmentation throughout the year. During periods of increased sun activity, age spots appear more intense and sharper compared to areas of the skin that are not affected by melasma. In the autumn-winter period, the influence of ultraviolet radiation from the sun's rays is not so pronounced, therefore, age spots become pale, less noticeable, and do not have such a pronounced border between areas of the skin unaffected by melasma.
Causes of Melasma
The leading role in the development of melasma is attributed to genetic predisposition.
The trigger factor can be:
- Pregnancy - often the pathology regresses within a few months after childbirth
- Hormonal contraceptives can also cause melasma, but hormone therapy during menopause does not cause melasma.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun or solarium
- Cosmetics containing photosensitizers
Prognosis
Reverse regression of melasma is possible several months after childbirth or cessation of breastfeeding. The problem with melasma is that it responds rather slowly to treatment and requires long-term qualified medical supervision.
Prevention
It is necessary to use sunscreen filters of a wide range of protection. Optimal use of SPF 30 and higher. Sunscreen should be applied daily, whether the person goes outside or not. It can also be treated well with whitening creams or prescription drugs.
Melasma Treatment
- Cancellation of hormonal contraceptives, if a woman takes them, is an important point in the treatment of melasma.
- Avoid taking medications, food additives and photosensitizing foods.
- Applying sunscreen all year round. Sunscreens should have a broad spectrum of protection - UVB + UVA.
- Do not use powerful skin cleansers (often used to treat or prevent acne).
- Be careful when using cosmetics containing retinoids, α-hydroxy acids, β-hydroxy acids (AHA, BHA). Consultation with a specialist is required.
- Avoid overdrying the skin as the skin produces its own SPF.
- The use of cosmetics inhibiting melanogenesis:
- Pigment Gel PCA Skin
- Kojic acid
- azelaic acid (may be used during pregnancy)
- Topical corticosteroids - provide a fairly rapid clinical effect, especially in cases where the appearance of melasma is associated with inflammation in the skin.
- Topical retinoids (contraindicated during pregnancy).
- Exfoliating Techniques:
- Chemical peels (should only be performed by a doctor, since a certain rehabilitation regimen must be observed):
- Jessner Peels with Hydroquinone
- Salicylic acid.
- Hydroxy acids - glycolic, lactic, etc.
- Retinoic peeling.
- Microdermabrasion. The disadvantage is the unevenness of the impact in depth. Preferred laser peels with adjustable depth- SilkPeel.
- Laser pilling - preference should be given to "cold lasers" - erbium lasers (Er: YAG 2940nm). MicroLaserPeel procedure. A good effect will be achieved with the epidermal type of melasma. Lasers with pronounced coagulation (warming up), such as CO2 laser, non-ablative fractional lasers, are often the cause of hyperpigmentation themselves. This is one of the possible side effects.
- Fractional rejuvenation. If the pathology has dermal localization, the best results will be achieved by fractional skin rejuvenation with a ProFractional erbium laser (Er: YAG 2940nm), since fractional destruction of deep-seated pigment is possible in this case and, secondly, treatment will be combined with microfenestration - the formation of microchannels, through which the pigment will be easily removed from the deep layers (dermis, papillary layer).
- New - HALO laser - the first hybrid fractional laser allows in one procedure to affect different levels of pigment deposition - on dermal, deep-lying pigment and epidermal, superficial pigment.
- Chemical peels (should only be performed by a doctor, since a certain rehabilitation regimen must be observed):
- Photorejuvenation. These techniques are currently the best choice for the correction of pigmented formations, as they allow you to destroy the pigment without compromising the integrity of the skin. The disadvantage is the difficulty of removing deep-seated age spots (dermal form).
- Oral intake of proanthocyanidins. Proanthocyanidins (proanthocyanidin, procyanidins) are a natural component and allow you to achieve good results, both in monotherapy and in combination with other methods of treatment. They will be indispensable in case of intolerance to other drugs.
Prognosis
The melasma cure effect is slow to be achieved. Complete elimination of melasma can be achieved only in 30% of cases. In other cases, a stable remission is achieved, but with contact with the sun or with a change in hormonal levels, regression of symptoms is possible.