Hirsutism: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Hirsutism (hirsutism) is a condition in women that results in excessive growth of dark or coarse male-patterned hair on the face, chest and back.
Hirsutism should be distinguished from hypertrichosis (see below). In hirsutism, excess hair growth is often due to excess male hormones (androgens), primarily testosterone.
Self-help methods and effective treatments are available for women seeking a cure for hirsutism.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of hirsutism are coarse or dark body hair, appearing in places where women usually do not have hair - mainly on the face, chest, lower abdomen, inner thighs and back. Opinions differ widely on what is considered excessive.
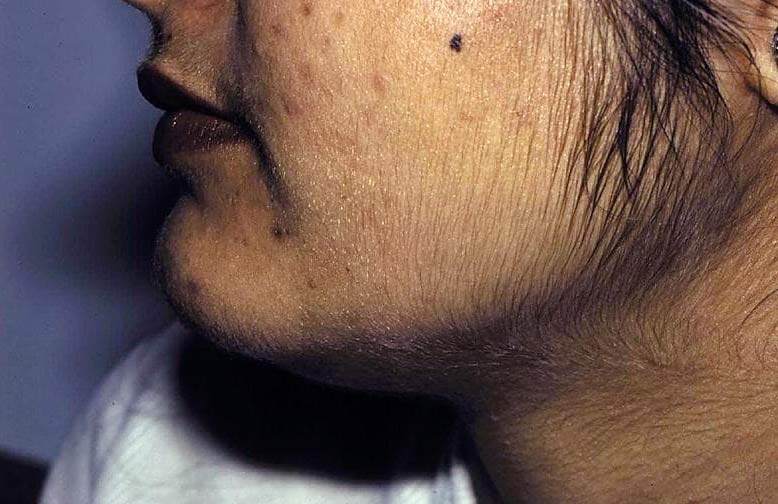
When high androgen levels cause hirsutism, other symptoms may appear over time - a process called virilization. Signs of virilization may include:
- Lower your voice
- Hair loss
- Acne
- Breast reduction
- Increase muscle mass
- Clitoris enlargement
When to see a doctor?
If you think you have too much coarse facial or body hair, talk to your doctor about your treatment options.
Excessive facial or body hair is often a symptom of an underlying medical problem. See your doctor if you have experienced strong or rapid growth of facial or body hair or signs of virilization for several months. You may be referred to a doctor who specializes in hormonal disorders (endocrinologist), genital dysfunction (gynecologist), or skin problems (dermatologist). Do not self-diagnose and self-medicate - see a doctor!
Causes
Hirsutism is a fairly common problem and occurs in 10% of the female population. Hirsutism can be caused by:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. This disorder, which often begins during puberty, causes an imbalance in sex hormones. Over the years, PCOS can gradually lead to excess hair growth, irregular periods, obesity, infertility, and sometimes multiple ovarian cysts.
- Cushing's Syndrome. This happens when the level of the hormone cortisol rises in the body. It can develop because your adrenal glands produce too much cortisol or because of long-term use of medications such as prednisone.
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. This inherited disorder is characterized by abnormal production of steroid hormones, including cortisol and androgens by the adrenal glands.
- Tumors. In rare cases, hirsutism can be caused by an androgen-secreting tumor in the ovaries or adrenal glands.
- Medical hirsutism. Some medicines can cause hirsutism. These include minoxidil (Minoxidil, Rogaine); Danazol, which is used to treat women with endometriosis; testosterone (Androgel, Testim) and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). If your partner uses topical products containing androgens, you may also suffer from skin-to-skin contact.
Hirsutism often occurs without an established cause.
Risk Factors
Several factors can influence the likelihood of developing hirsutism, including:
- Family history. Several diseases that cause hirsutism, including congenital adrenal hyperplasia and polycystic ovary syndrome, are inherited.
- Ethnicity. Women of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern and South Asian descent have more body hair for no known reason than other women.
- Obesity. Obesity causes increased production of androgens, which can worsen hirsutism.
Complications
Hirsutism can cause emotional distress. Some women are embarrassed about having unwanted hair. Some develop depression. In addition, while hirsutism does not cause physical complications, the underlying cause - hormonal imbalances - can cause them.
If you have hirsutism and irregular periods, you may have polycystic ovary syndrome, which can interfere with fertility. Women taking certain medications and for the treatment of hirsutism, pregnancy should be avoided due to the risk of birth defects.
Treatment of hirsutism
Treatment of hirsutism is divided into pathogenetic - elimination of the cause and symptomatic - the fight against manifestations, that is, with unwanted hair.
Laser hair removal for hirsutism
Laser hair removal for hirsutism is the most effective and safest method. Due to the action of the laser, the hair follicle is destroyed and hair growth stops. The laser acts selectively on the hair, so the treatment is safe for the surrounding tissues and the body as a whole.

Electrolysis
Electrolysis is also a permanent method of removing unwanted hair, just like laser hair removal. The advantage of electrolysis is that it can be performed on light and gray hair, unlike a laser. The negative aspects include discomfort during the treatment, a high risk of complications such as scarring.
Temporary Hair Removal Techniques
As a temporary and short-term solution to the problem of hirsutism, use: wax depilation, sugaring, hair removal with threads, home depilatory creams, growth retarding creams hair, shaving, etc. After a while, hair growth will resume.
Prevention
Hirsutism is usually not preventable. But losing weight while being overweight can help reduce the appearance of hirsutism, especially if you have polycystic ovary syndrome.
Materials used
- Hirsutism, www.mayoclinic.org
- Hirsutism, www.emedicine.medscape.com